GameNGen, a neural model-based game engine, is demonstrating the potential to revolutionize how video games are generated and played. An innovative approach developed by Google Research and Tel Aviv University researchers allows for real-time interaction with complex gaming environments without relying on traditional game engines.
As the authors reported, GameNGen can simulate the classic game DOOM at over 20 frames per second, achieving visual quality comparable to the original game.
The core of GameNGen’s functionality lies in its use of diffusion models, a type of generative AI that has become a standard in media generation. The process begins with training a reinforcement learning (RL) agent to play the game, recording its actions and observations. This data is then used to train a diffusion model to predict the next frame based on a sequence of past frames and actions. This method allows the model to simulate complex game state updates, such as managing health and ammo, attacking enemies, and interacting with the environment over long trajectories.
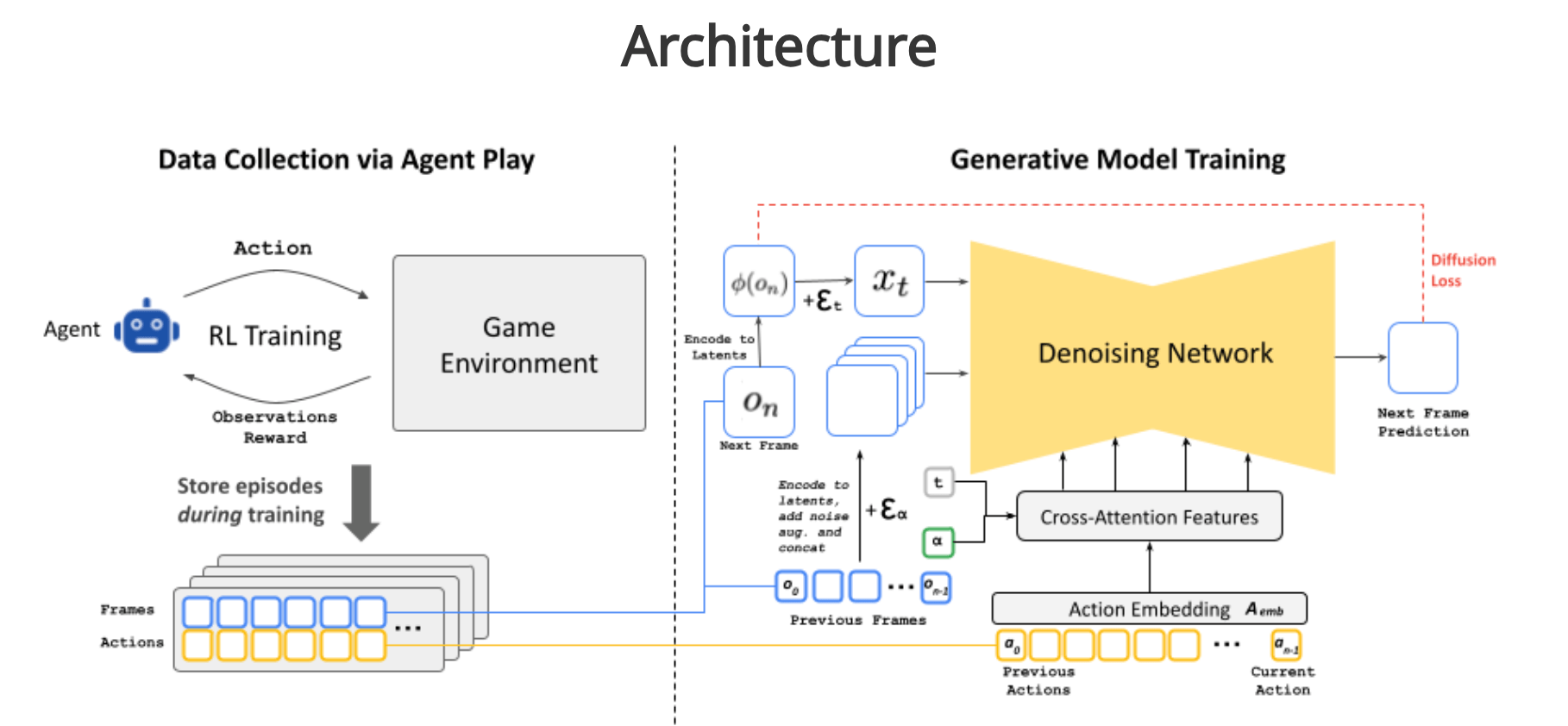
GameNGen’s approach addresses the challenges of simulating interactive worlds, which require conditioning on a stream of input actions available only during generation. The model achieves stable auto-regressive generation over long sequences by employing conditioning augmentations, mitigating issues like sampling divergence that can arise in such simulations.
The future of gaming could be AI-generated
Looking ahead, this proof of concept suggests several potential advancements in the gaming industry. AI models like GameNGen could lead to the development of games that are generated rather than manually coded, similar to how images and videos are produced by neural models today. This could make game development more accessible and cost-effective, allowing creators to design and modify games through textual descriptions or example images rather than traditional programming.
Moreover, AI models’ ability to simulate interactive environments in real-time could enhance games’ realism and interactivity. As AI methodology advances, it may enable the creation of more immersive and adaptive gaming experiences, where NPCs exhibit lifelike behaviors and environments respond dynamically to player actions. This could lead to richer storytelling and more engaging gameplay as AI-driven games adapt to individual player preferences and skill levels.
Additionally, the integration of AI in game development could facilitate the procedural generation of content, allowing developers to create diverse and expansive game worlds with less manual effort. This could result in endless replayability and unique player experiences as AI models generate new levels, quests, and challenges based on player interactions and preferences.
The future of AI in gaming also holds promise for enhanced game analytics and player experience modeling. By leveraging AI’s predictive capabilities, developers could gain insights into player behavior and preferences, enabling them to better tailor game mechanics and difficulty levels in real-time. This data-driven approach could lead to more personalized and engaging gaming experiences and improved game performance and player retention.
While GameNGen is currently demonstrated on DOOM, its creators envision applying this technology to other games and interactive software systems, highlighting the potential for broader applications in the gaming industry. The ongoing research aims to refine the model’s capabilities, such as expanding its memory and improving its ability to handle more complex environments, further enhancing the realism and interactivity of AI-generated games.
The post AI model generates real-time playable DOOM with no game engine appeared first on CryptoSlate.





