Bitcoin protects private property for its users due to its theft-proof design, its use of decentralized nodes and an immutable public ledger.
We’re going to continue our conversation of Bitcoin’s role in humanitarianism, this time in the realm of private property rights. But before we talk about that, we need to understand why private property is so important.
One of the biggest drivers of economic growth and higher standards of living is private property rights.
This is the idea that you own the fruits of your labor as well as anything else you purchase with the fruits of your labor. To illustrate this, let’s say you are working at a company and you save enough money to buy a car. The money you earn (which is the fruit of your labor) and the car are both your property. The government has to protect your property from theft by other private individuals, and the government itself cannot take your property without due cause and/or just compensation.

Private property rights are important because they incentivize productivity. People are disincentivized to work if the money they earn or the stuff they buy can be confiscated without warning or compensation.

And in a society where people are disincentivized to work, there are fewer products and services available and less innovation occurring. These three factors are the key drivers in improving a region’s standard of living. Private property rights are the reason why there are better cars every year, better phones, computers and faster internet.
But, property rights don’t exist naturally. They have to be enforced by a government that punishes people for stealing other people’s property as well as not encroaching on its own citizen’s property. And, unfortunately, many countries around the world do not have a government that does this.
For example, the Chinese government will cut off people from Alipay and WeChat Pay, popular Chinese payment systems, if they make statements that go against the current authoritarian regime. Russia will freeze people’s bank accounts if they spread news that works against the Kremlin and its interests. And in 2021, Nigeria froze the bank accounts of citizens protesting against the government.
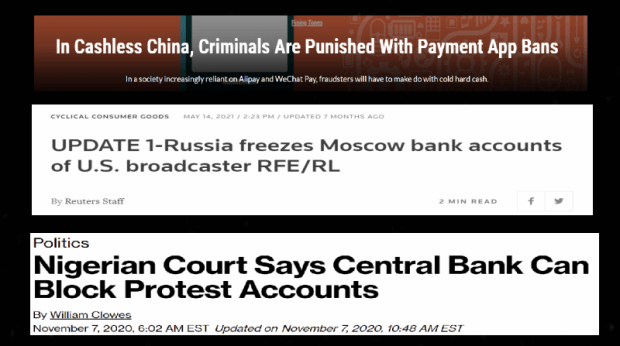
The lack of respect for private property harms these countries’ citizens and keeps them in a worse state of living relative to other freer countries. It’s not a coincidence that democratic countries are much wealthier than authoritarian countries.

How Does Bitcoin Protect Property Rights?
Bitcoin’s blockchain, by design, makes it impossible for private and public actors to take control of someone else’s money. The blockchain is immune to theft and unitary control because it is a decentralized system. The blockchain is spread across a network of computers, called nodes, and to control the blockchain, you would have to control at least 50% of the nodes in the network. This is a virtual impossibility because the amount of energy and resources needed to control 51% of the network would be insurmountable by any practical measure today. The blockchain has stood the test of time, in that 51% of it has yet to remain under the control of a single actor, and as the number of nodes grows, this becomes less and less likely to happen.
Citizens under an authoritarian government do not have to worry about the government stealing their bitcoin, nor do they have to rely on inept failing governments to protect their property.
For millions of people around the world, bitcoin is their first chance to practice self-sovereignty over their own money. Their money is under their control and they don’t have to worry about anyone stealing it. Bitcoin is helping them preserve the human right to private property.
This is a guest post by Siby Suriyan. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc. or Bitcoin Magazine.








